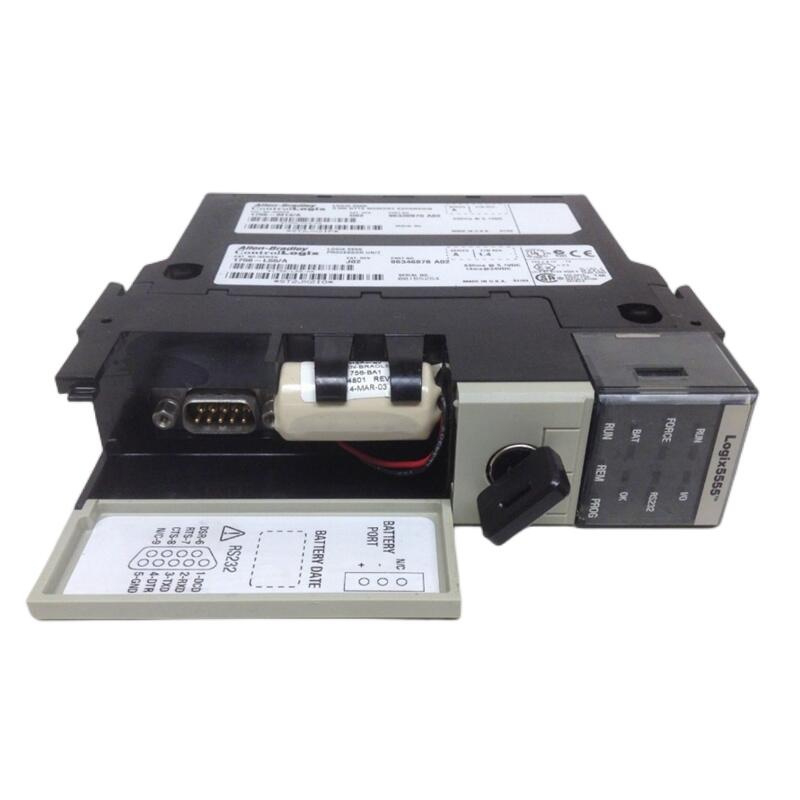
Allen-Bradley 1336-B007-EOD-L Device Module
Allen-Bradley 336-B007-EOD-L
1. Overview
2. Specifications
|
Parameter
|
Specification
|
|---|---|
|
Motor Power
|
1 HP (0.75 kW)
|
|
Power Supply Requirement
|
380-480 VAC (Three-Phase), 50/60 Hz
|
|
Input Current
|
Approx. 2.5 A (depending on specific power supply voltage)
|
|
Output Current
|
4 A (based on 1 HP specification)
|
|
Overload Device (EOD)
|
Built-in Electric Overload Device
|
|
Control Method
|
Vector Control (FOC), Sensorless Vector Control
|
|
Communication Interface
|
L Logic Ports (L1, L2, L3)
|
|
Dimensions
|
Compact design, easy to install in control cabinets or racks
|
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3. Product Features
4. Structure and Composition
5. Application Fields
6. Installation and Maintenance
Installation Notes
- Ventilation: Although small in size, the power module generates heat during operation. It is recommended to reserve sufficient heat dissipation space.
- Power Connection: Ensure the correct phase sequence of the input power supply; the wiring of the three-phase power supply must not be wrong.
- Ground Connection: Must be reliably grounded to prevent electromagnetic interference (EMI).
Maintenance
- Regular Inspection: Check the expansion of input power capacitors and whether internal wiring is loose.
- Fault Diagnosis: Use built-in fault codes (such as overload, overcurrent, short circuit, etc.) for quick troubleshooting.
- Firmware Update: If compatibility issues or performance requirements arise, contact the manufacturer for firmware upgrades.
————————————————————————————————————-
If you would like to learn more about our products and services, please feel free to contact us at any time!
- Sales Manager : Jinny
- Email : sales5@xrjdcs.com
- Whatsapp/Mobile:+86 15359273791
Global renowned brand cooperation
ABB 丨 GE 丨Allen Bradley 丨 Honeywell 丨 Emerson 丨 Bently Nevada 丨 Westinghouse
Triconex 丨 Foxboro 丨 ICS Triplex 丨 Hima 丨 Schneider 丨 Yokogawa 丨 Woodward
—————————————————————————————
________________________________________________【Delivery Time】
1. Express Shipping (DHL, UPS, FedEx, EMS):3-10 working days is a good rule of thumb. These services prioritize speed and often offer features like next-day or guaranteed delivery by a certain date (for an additional fee).
2. Air Mail (China Post, Hong Kong Post):7-35 working days, depending on the destination country. This is a more budget-friendly option, but it takes longer because it has lower priority for shipment.
【Important Notes】
Please follow the product’s instruction manual carefully for installation and debugging to avoid damage to the product.